Circular Economy
What is the circular economy model good for?
The circular economy model is a resilient system that is good for business, people and the environment. It integrates every stage of a product’s life cycle, from the moment it is designed until it becomes waste and how the recycling materials can be introduced in the manufacturing process.
Areas where the circular economy can be applied and developed are: biodiversity, city organization and management, climate, fashion, green energy, finance, food, waste and resources management.

Sustainability in an ever more populated world
The world’s population is growing, increasing the demand for raw materials that are finite and limited.
This scenario leads to the fact that some EU countries are dependent on other countries for their raw materials. Consequently, the extracting and using of raw materials has a major impact on the environment as well as increasing energy consumption and CO2 emissions.
What is the EU doing to promote a circular economy?
The European Commission presented the circular economy action plan in March 2020, to promote more sustainable product design, reduce waste and empower consumers (for example by creating a right to repair). The focus is on resource-intensive sectors, such as electronics and ICT, plastics, textiles, and construction.
One year later, the Parliament adopted a resolution on the new circular economy action plan demanding additional measures to achieve a carbon-neutral, environmentally sustainable, toxic-free and fully circular economy by 2050, including tighter recycling rules and binding targets for materials use and consumption by 2030.
The first package of measures was released in 2022 to speed up the transition towards a circular economy, as part of the circular economy action plan. The proposals include stimulating sustainable products, empowering consumers for the green transition, reviewing construction product regulations, and creating a strategy for sustainable textiles.
Extending the life cycles of products
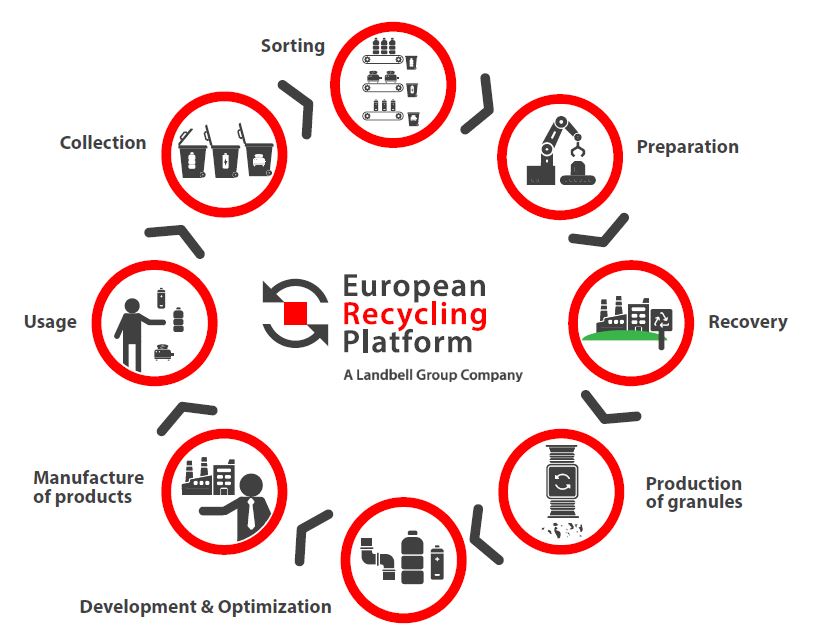
The circular economy is a production and consumption model involving sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling existing materials and products as long as possible.
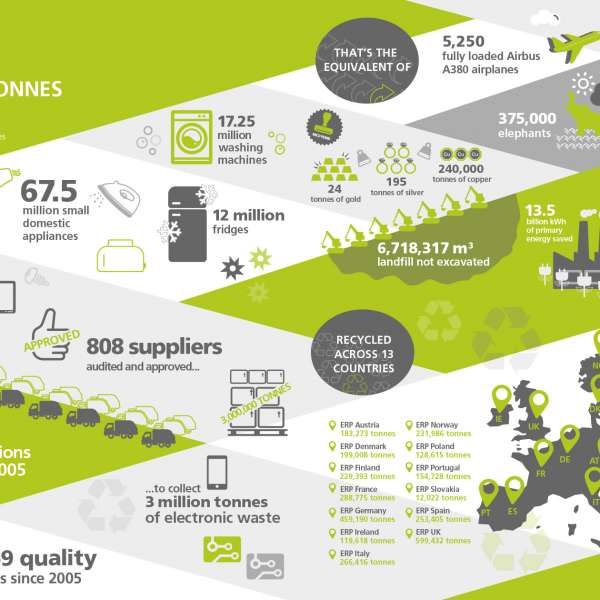
Annually, more than 2.5 billion tonnes of waste are produced in the European Union. This number introduces the need to urgently promote a more sustainable model as the circular economy, directly connected to the legislation on waste management, where ERP plays an important role.
The circular economy is the model for the future
The circular economy model is different from the linear economy model, which was based on a take-make-consume-throw-away pattern, where excessive and unnecessary consumption was seen as the right behaviour.
The circular economy focuses on sharing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling instead. The result being that the life cycle of products is extended and the waste is reduced to a minimum, as its materials are kept within the economy wherever possible by reusing them to create further value.
Circular Economy
What are the benefits of a circular economy?
1. Waste prevention, ecodesign, and reuse could save EU companies money while also reducing the total annual greenhouse gas emissions. Nowadays, the production of materials we use account for 45% of CO2 emissions.
3. Reducing pressure on the environment, improving the security of the supply of raw materials, increasing competitiveness, stimulating innovation, energizing economic growth (an additional 0.5% of gross domestic product), and creating jobs (700,000 jobs in the EU alone by 2030).
Services
How can ERP support a circular economy?
Recycling transforms waste into resources (secondary raw materials) to be used in new product manufacturing. Innovative solutions to recycle waste and keep it in the loop has been one of ERP and Landbell’s commitments for over 15 years
Treatment of hazardous substances can avoid the contamination of soils, water and air and reduce atmosphere pollution
Invest in awareness campaigns to awaken circular behaviour by companies, associations and the population in general
News
October 14th, 2022
“Recycle it all, no matter how small”
News
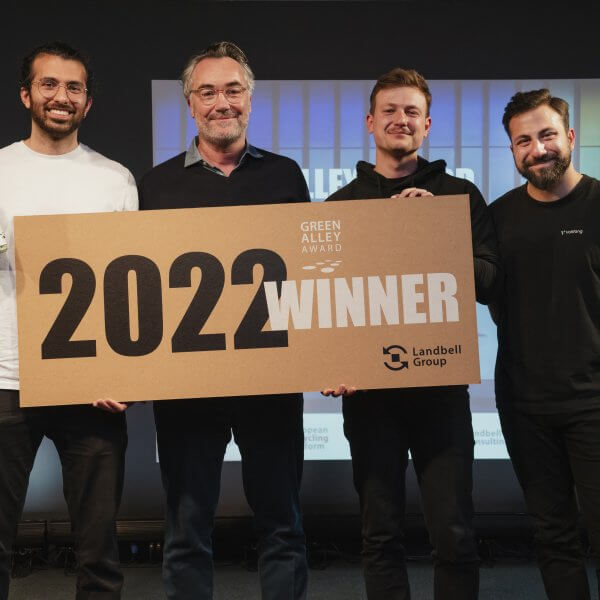
May 2nd, 2022
This year’s Green Alley Award goes to the German start-up Voltfang
News
September 28th, 2021
It’s official: we've reached 4 million tonnes of electronic waste collected.
News
July 20th, 2021
New report commissioned by ERP finds competition is beneficial to circular economy.
News
August 1st, 2018
The Green Electronic Council formally recognizes Landbell Group's new audit standard for WEEE Treatment
News
July 25th, 2018
ERP urges European Commission to reconsider legislative proposal
News
April 18th, 2018
European Union paves the way for a stronger and more competitive circular economy
News
November 29th, 2017
ERP's review includes status of transposition in each Member State
News, Video
November 22nd, 2017
New film outlines Landbell Group's vision for the circular economy
News
November 10th, 2017
Sulapac from Finland wins circular economy prize
News
October 19th, 2017
Six companies invited to Berlin in November
News
September 21st, 2017
ERP UK’s new report looks at a decade of continual evolution since the WEEE Regulations were first introduced in the
News
March 23rd, 2017
Revision of the EU Waste Legislation and Circular Economy Package
News, Video
January 12th, 2017
DHL and Landbell Group Announce Strategic Partnership
News
June 8th, 2016
for regulatory waste management framework
News
April 6th, 2016
ERP supports consistent, constructive solutions for EPR schemes across Europe
News
March 22nd, 2016
for the end-of-life management of IT and Display equipment
News
February 23rd, 2016
News
September 14th, 2015
Ambitious, Competitive and Cost Effective
News
July 13th, 2015
on electronic devices on September 1, 2015
News, Video
May 15th, 2015
Umberto Raiteri, President and CEO of ERP SAS, on Euro Parliament Network HSE24